1. Disable IPv6 using Sysctl
First of all, you can check if you have IPv6 enabled with:
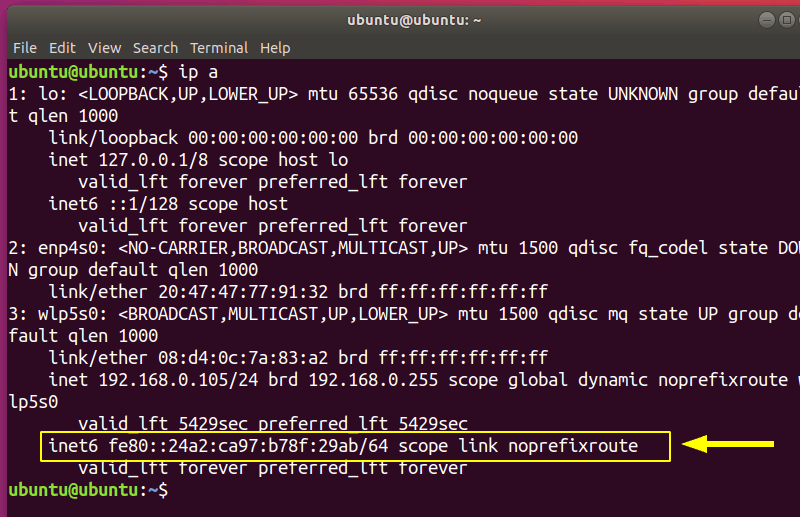
ip a
You should see an IPv6 address if it is enabled (the name of your internet card might be different):
You have see the sysctl command in the tutorial about restarting network in Ubuntu. We are going to use it here as well. To disable IPv6 you only have to input 3 commands:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1 sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1
You can check if it worked using:
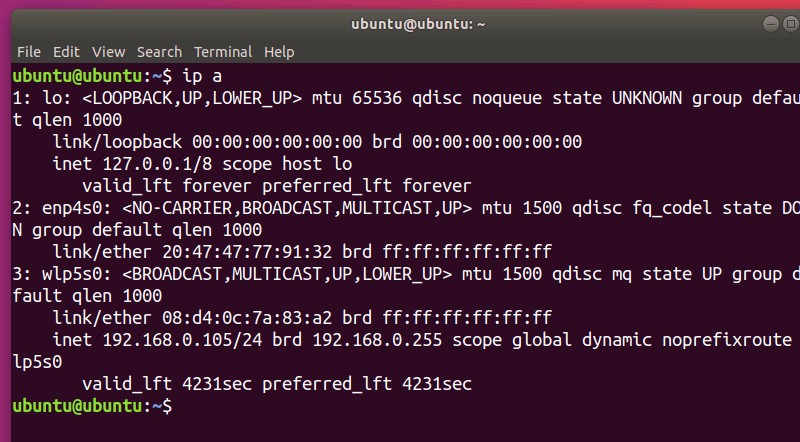
ip a
You should see no IPv6 entry:
However, this only temporarily disables IPv6. The next time your system boots, IPv6 will be enabled again.
One method to make this option persist is modifying /etc/sysctl.conf. I’ll be using vim to edit the file, but you can use any editor you like. Make sure you have administrator rights (use sudo):
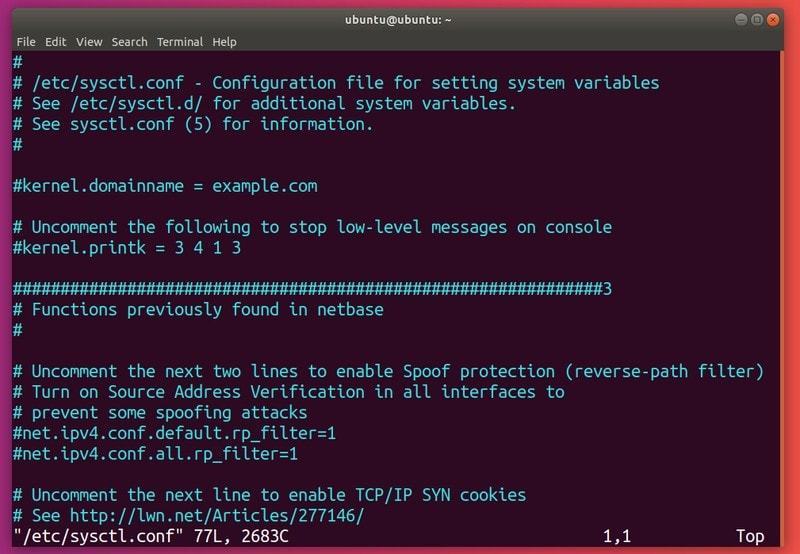
Add the following lines to the file:
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1
For the settings to take effect use:
sudo sysctl -p
If IPv6 is still enabled after rebooting, you must create (with root privileges) the file /etc/rc.local and fill it with:
#!/bin/bash # /etc/rc.local
/etc/sysctl.d /etc/init.d/procps restart
exit 0
Now use chmod command to make the file executable:
sudo chmod 755 /etc/rc.local
What this will do is manually read (during the boot time) the kernel parameters from your sysctl configuration file.
2. Disable IPv6 using GRUB
An alternative method is to configure GRUB to pass kernel parameters at boot time. You’ll have to edit /etc/default/grub. Once again, make sure you have administrator privileges:
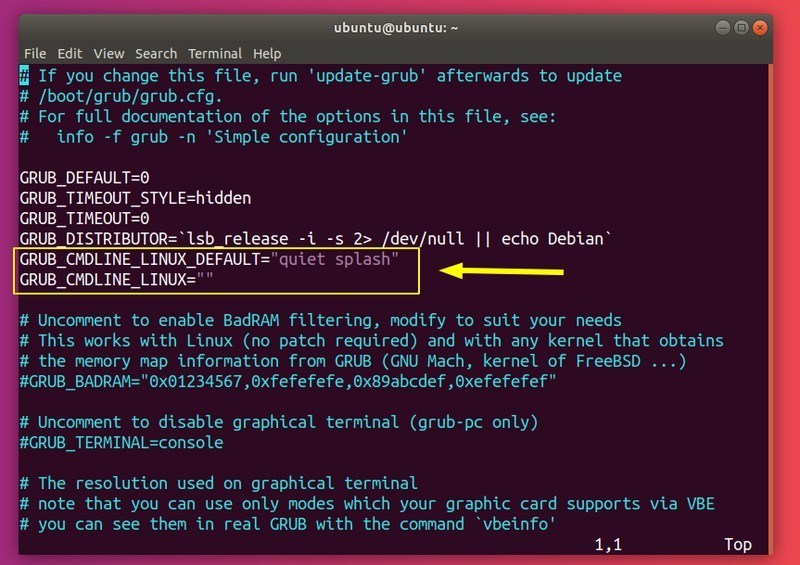
Now you need to modify GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT and GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX to disable IPv6 on boot:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash ipv6.disable=1" GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="ipv6.disable=1"
Save the file and run:
sudo update-grub
The settings should now persist on reboot.
Re-enabling IPv6 on Ubuntu
To re-enable IPv6, you’ll have to undo the changes you made. To enable IPv6 until reboot, enter:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=0 sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=0
Otherwise, if you modified /etc/sysctl.conf you can either remove the lines you added or change them to:
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=0 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=0
You can optionally reload these values:
sudo sysctl -p
You should once again see a IPv6 address:
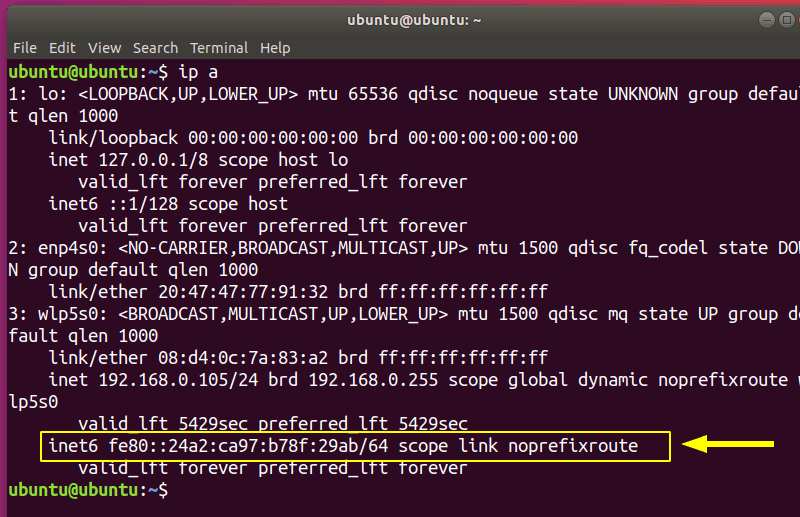
Optionally, you can remove /etc/rc.local:
sudo rm /etc/rc.local
If you modified the kernel parameters in /etc/default/grub, go ahead and delete the added options:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash" GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
Now do:
sudo update-grub
Wrapping Up
In this guide, I provided you ways in which you can disable IPv6 on Linux, as well as giving you an idea about what IPv6 is and why you would want to disable it.



























