Htop is an interactive real-time process monitoring application for Linux/Unix like systems and also a handy alternative to top command, which is default process monitoring tool that comes with pre-installed on all Linux operating systems.
Htop has numerous other user-friendly features, which are not available under the top command and they are:
- In htop, you can scroll vertically to view the full process list and scroll horizontally to view the full command lines.
- It starts very quickly as the compared top because it doesn’t wait to fetch data during startup.
- In htop, you can kill more than one processes at once without inserting their PIDs.
- In htop, you no longer needed to enter the process number or priority value to re-nice a process.
- Press “e” to print the set of environment variables for a process.
- Use the mouse to select list items.
Install Htop Using Binary Packages in Linux
Important: Following binary installation, will give you the available htop version 1.0.3 or 1.0.2 in most distributions, so if you’re looking for Htop 2.0.2 version, then I recommend you to follow Source installation section as shown below:
To install Htop on RHEL 7/6/5 and CentOS 7/6/5, your system must have EPEL repository installed and enabled, to do so run the following commands on your respective distributions to install and enable it for your system architecture (32bit or 64bit).
On RHEL/CentOS – 32-bit OS
-------------- For RHEL/CentOS 6 -------------- # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -ihv epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm -------------- For RHEL/CentOS 5 -------------- # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm # rpm -ihv epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
On RHEL/CentOS – 64-bit OS
-------------- For RHEL/CentOS 7 -------------- # wget dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/e/epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpm # rpm -ihv epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpm -------------- For RHEL/CentOS 6 -------------- # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -ihv epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm -------------- For RHEL/CentOS 5 -------------- # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/x86_64/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm # rpm -ihv epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
Once EPEL repository has been installed, you can hit the following yum command to fetch and install the htop package as shown.
# yum install htop
On Fedora OS
Fedora users can easily install htop using Fedora Extras repository by typing:
# yum install htop # dnf install htop [On Fedora 22+ releases]
On Debian and Ubuntu
In Debian and Ubuntu, you can fetch htop by typing:
# sudo apt-get install htop
Compile and Install Htop from Source Packages
To install Htop 2.0.2 version, you must have Development Tools and Ncurses installed on your system, to do so run the following series of commands on your respective distributions.
On RHEL/CentOS and Fedora
# yum groupinstall "Development Tools" # yum install ncurses ncurses-devel # wget http://hisham.hm/htop/releases/2.0.2/htop-2.0.2.tar.gz # tar xvfvz htop-2.0.2.tar.gz # cd htop-2.0.2
On Debian and Ubuntu
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential $ sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev $ wget http://hisham.hm/htop/releases/2.0.2/htop-2.0.2.tar.gz $ tar xvfvz htop-2.0.2.tar.gz $ cd htop-2.0.2
Next, run the configure and make the script to install and compile htop.
# ./configure # make # make install
How do I use htop?
Now run the htop monitoring tool by executing following command on the terminal.
# htop
Htop is having three sections mainly
- Header, where we can see info like CPU, Memory, Swap and also shows tasks, load average and Up-time.
- List of processes sorted by CPU utilization.
- Footer shows different options like help, setup, filter tree kill, nice, quit etc.
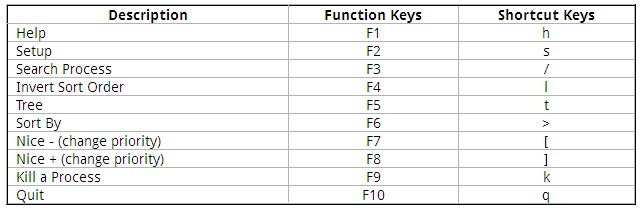
Htop Shortcut and Function Keys
Some of the shortcut and function keys and its functionality to interact with htop.